How Germany Deals with Smartphone Use in Schools
The issue of smartphone usage in German schools continues to spark debate, with the state of Bavaria implementing stringent bans on the technology whilst areas such as Lower Saxony allows schools the discretion to decide on their own rules.
- Bavaria enforces ban on smartphones
- Lower Saxony allows individual schools decide
- German-speaking Belgium schools also ban phones
- Some schools allowing phones for education purposes
- Meanwhile, UN reports 60 countries now have school phone bans
As parental involvement is vital in shaping these policies, The Institute for Applied Social Sciences conducted a survey for the Robert Bosch Stiftung Foundation revealing that 76% of German parents support banning smartphones in order to reduce distractions, enhance social development and mitigate the risks associated with excessive media consumption. Although some opinions were divided regarding these bans in secondary schools, there was a consensus on limiting them in elementary education.
This leaves both parents and educators at a crossroads where they must weigh up the advantages of digital literacy in education against the potential for distraction and dependency, bearing the question; should Germany enforce country wide measures like in Bavaria or continue allowing schools to implement their own policies?
Divided Opinions in Germany
While on the surface the benefits of a country wide phone ban in schools seems obvious, there are contrasting arguments from parents, teachers and law makers, with some suggesting that the technology can be a valuable education tool and prohibiting them has the potential to hinder digital literacy.
Despite these objections it is evident that this ban will help to alleviate some parental concerns by fostering a more focused learning environment that enhances educational benefits and proper social development. As smartphones are a primary source of distraction and have the potential to undermine students’ ability to concentrate, the removal of these devices in schools will not only help pupils maintain focus but assist in mitigating issues such as cyberbullying and unauthorised content sharing, ultimately creating a safer school environment.
This underlines the benefits of implementing such a policy and these measures have the potential to innovate the entire country’s educational framework. Similar initiatives have been shown to make a significant impact when introduced in places such as Australia and other EU Countries which demonstrates evidence-based research to support the replication of such policies in Germany.
How can schools implement a Phone Ban?
Of course, there are complexities to this sort of ban, and it is important to evaluate the nuances of modern education in which technology plays a pivotal role – some of which are unique to German schools.
Some against the ban argue that prioritising parental responsibility can make it a more collaborative approach, ensuring both schools and families guide students in responsible phone usage to establish an appropriate technology balance.
It is further noted that allowing controlled access of smartphones can enhance student autonomy, empowering them to make informed decisions about their digital behaviour as well as enabling teachers to integrate technology into the classroom.
Seeing 100s of schools across Europe implement bans, our recommended essential steps include:
- Establishing clear rules on smartphone use
- Involve students and parents from the beginning
- Teach skills for using digital media safely to improve buy-in
- Consider a trial period
We share more in our dedicated article on how to have an effective phone ban in schools. There are also templates to amend you school’s policy available from the Rhineland-Palatinate Educational Institute, and the Bavarian State Ministry of Education and Cultural Affairs has shared good practice on their website.
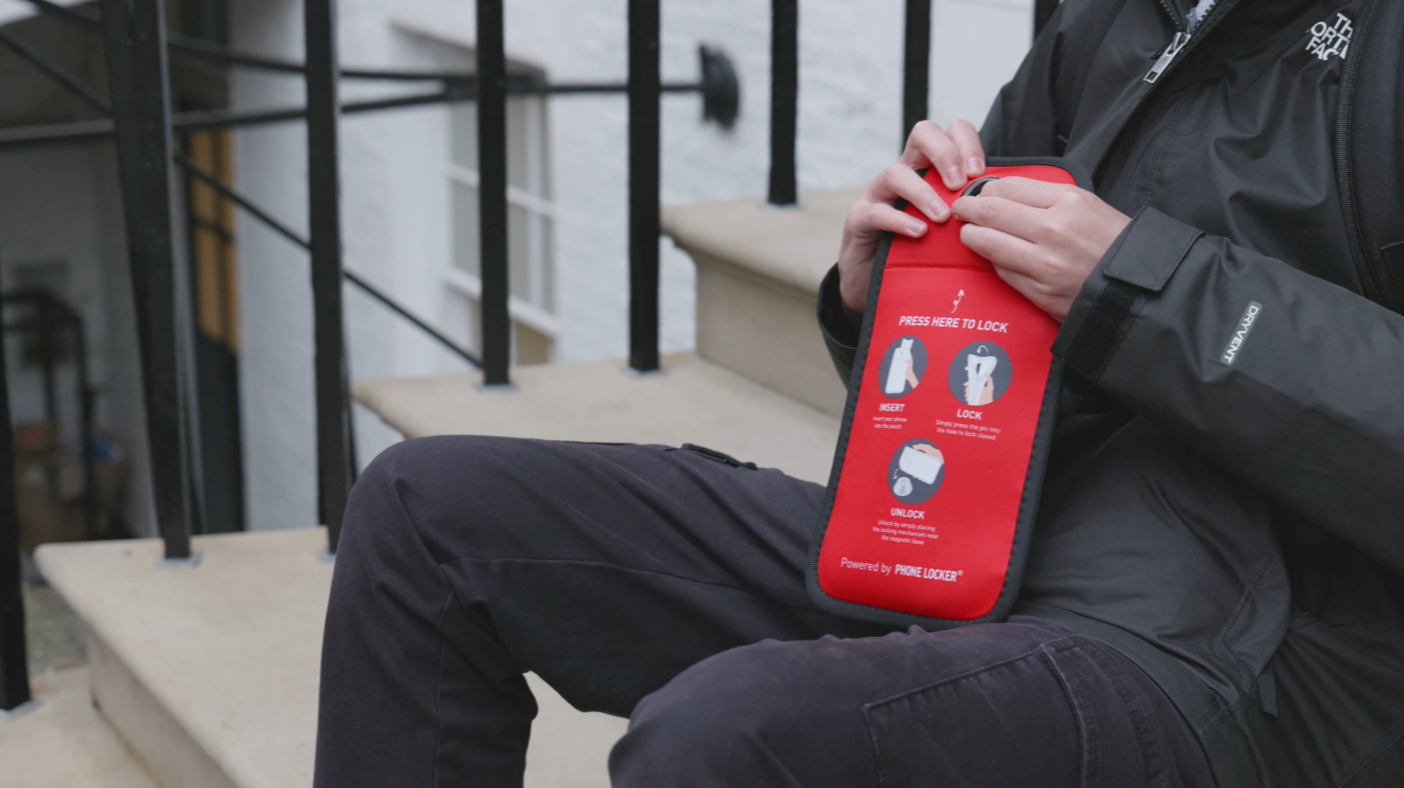
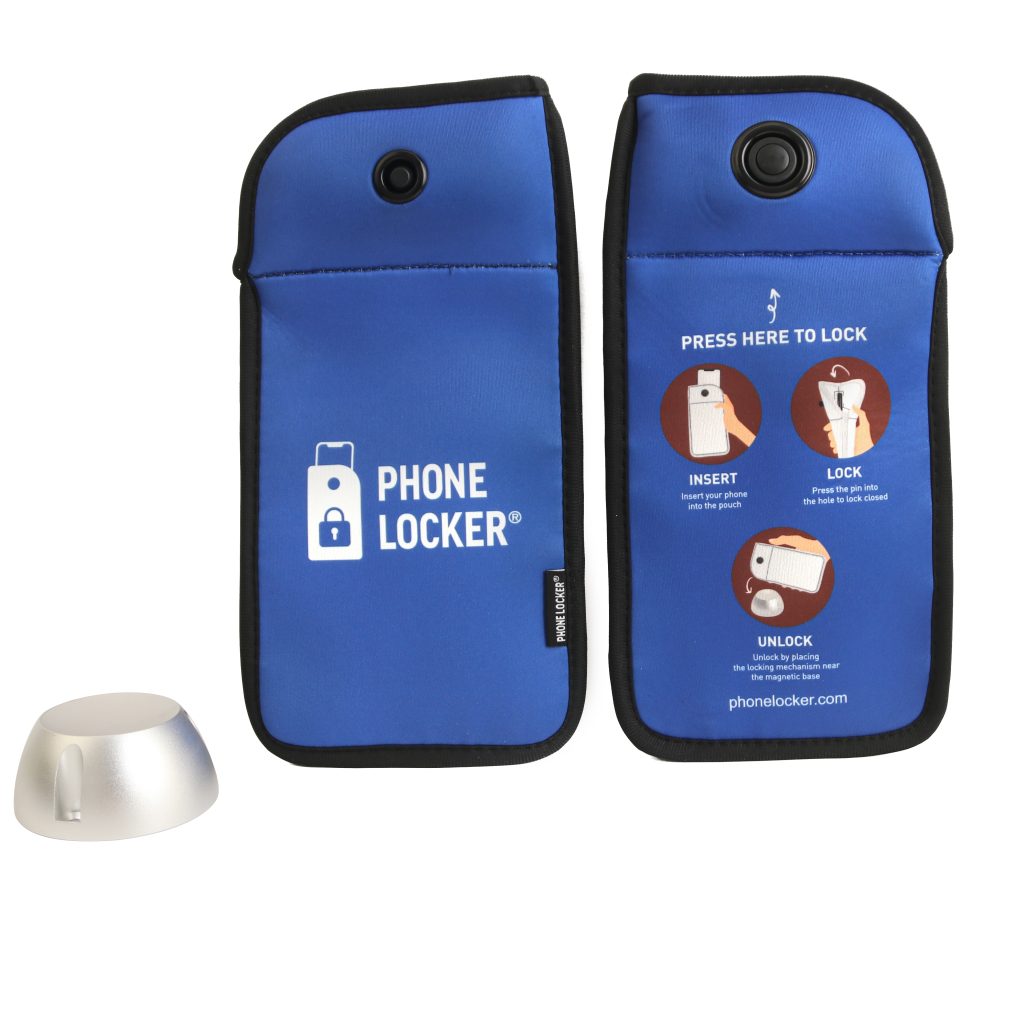
Some teachers who are nervous against an outright phone ban at their school due to confrontation with pupils, or difficulties in enforcing the ban, are finding the integration of Phone Locker® lockable phone pouches can help resolve many of the drawbacks that come with the ban by allowing users to retain possession of their phone throughout the day.
If you’re interested in creating a phone-free environment with a technology ban solution that is used by schools and venues internationally then see How they work or get in touch for a quotation.

How are other countries approaching Phone Bans?
Ultimately, the decision to ban smartphone should be guided by ongoing research and aim to harmonise educational benefits while minimising distractions and this movement is gaining traction across the world:
France has now implemented a thorough ban on mobile phones in primary and middle schools, aiming to enhance academic performance and reduce interruptions.
Whereas Denmark and Italy lean towards controlled technology integration and early media education, but this approach heavily emphasises parental involvement, encouraging and relying on parents to regulate usage outside of school hours.
The UK is also exploring various actions, with parliamentary measures to be reviewed in March 2025 and tighter legislations regarding phone use for children on the horizon.
Belgium has similar bans on smartphones as French-speaking schools in Wallonia and Brussels are already operating with these restrictions in place and smartphones are proposed to be banned from German speaking schools in Belgium come September 2025.
Across the countries, a common thread is the acknowledgement of smartphones’ impact on academic performance and while the methods of prevention vary, the focus remains on creating an environment conducive to learning, where technology serves as an aid rather than a hindrance.
To effectively manage smartphone usage in German schools, the implementation of Phone Locker® pouches presents a promising solution. By providing a structured approach to phone management it enables teachers, parents, and students to experience the full benefits of a phone-free environment in education.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do Smartphone Bans Impact Student-Teacher Communication?
A study revealed 80% of teachers experienced fewer classroom distractions post-ban. These changes can positively impact academic performance and enhance social interactions among students.
Are There Any Exceptions to Smartphone Bans for Emergency Situations?
Exceptions to smartphone bans typically involve parental consent and teacher discretion, adhering to established emergency protocols. School policies prioritize student safety, ensuring that smartphones may be used when necessary to maintain a secure learning environment.
What Alternatives to Smartphones Are Suggested for Educational Purposes?
Tablet integration, interactive whiteboards, e-learning platforms, digital textbooks, and virtual reality simulations are suggested alternatives, enhancing educational experiences through innovative technology while maintaining focus and reducing distractions in the classroom.
How Do Smartphone Policies Address Special Needs Students?
Smartphone policies for special needs students emphasize inclusive accommodations, accessibility considerations, and individualized support plans. They incorporate assistive technology options and appropriate supportive resources to guarantee equitable access to educational opportunities.
Are There Any Studies on the Psychological Effects of Smartphone Bans on Students?
A recent study revealed that students experienced improved academic performance and better social interactions post-smartphone ban, notably enhancing mental health, attention span, working memory and behaviour management both in and out of educational environments.










