15 fatos: por que as escolas deveriam ficar 'sem telefone'
Quando as crianças começaram a ter smartphones, uma década atrás, não havia nenhuma pesquisa sobre seu impacto. Hoje, os smartphones são inescapáveis. De acordo com a Ofcom, 98% de crianças entre 16 e 17 anos possuem um smartphone no Reino Unido, quase 50% de menores de 13 anos estão agora nas mídias sociais e 90% de crianças possuem um telefone celular quando chegam aos 11 anos.
Nos últimos anos, a investigação ganhou força e os resultados são impressionantes, desencadeando uma resposta dos governos locais e centrais para tomarem medidas o mais rapidamente possível. a opinião pública esquenta com a fácil exposição das crianças ao mundo adulto.
Precisa de convencimento? Compilamos 15 trechos de pesquisas e estudos recentes sobre o tópico dos impactos dos smartphones em crianças em idade escolar, bem como o impacto de escolas que estão deixando de usar celulares.
83% dos pais acreditam que os smartphones são potencialmente prejudiciais aos jovens.
Fonte: Parent Kind
1 em cada 4 jovens adultos mostra sinais de dependência comportamental em smartphones.
Fonte: Kings College London
Jovens de 12 a 15 anos passam em média 35 horas por semana – o equivalente a um emprego de tempo integral – em seus smartphones.
Fonte: Universidade de Birmingham
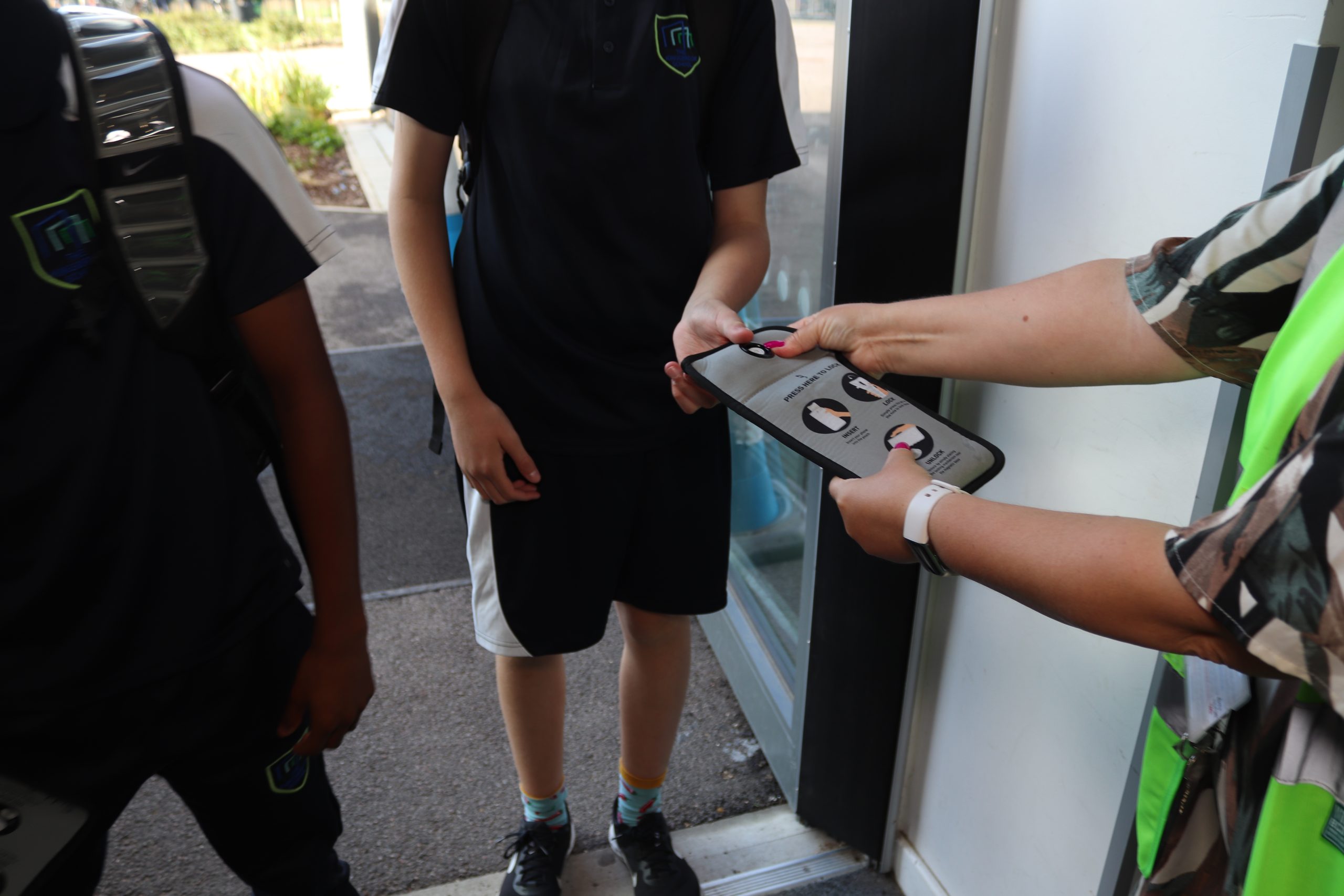
Apenas 11% das escolas secundárias têm proibições efetivas de uso de telefone.
Fonte: Policy Exchange
Pode levar até 20 minutos para que os alunos se concentrem novamente no que estavam aprendendo quando estavam distraídos.
Fonte: Universidade de Chicago

1 em cada 3 professores relata que os alunos usam celulares nas aulas sem permissão.
Fonte: Departamento de Educação
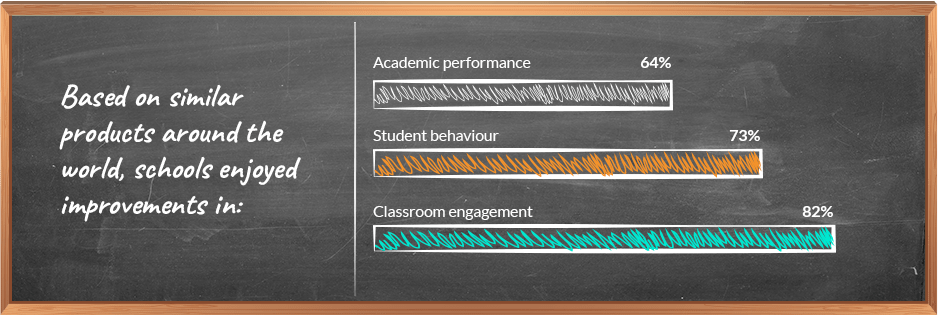
Foi descoberto que a remoção de smartphones de escolas na Bélgica, Espanha e Reino Unido melhorou os resultados de aprendizagem.
Fonte: UNESCO
Dados mostram que quanto mais cedo eles ganharam seu primeiro smartphone, pior sua saúde mental hoje.
Fonte: Sapien Labs
Jovens que sofrem cyberbullying têm duas vezes mais chances de tentar suicídio e se automutilar.
Fonte: Publicações JMIR
Os casos de cyberbullying estão aumentando, com 1 em cada 6 crianças afirmando ter sofrido cyberbullying.
Fonte: Organização Mundial da Saúde

90% de meninas e 50% de meninos dizem que recebem conteúdo explícito que não querem ver.
Fonte: Ofsted
O tempo médio diário que os adolescentes passam com os amigos caiu 65% desde 2010.
Fonte: Science Direct
Após apenas 3 semanas, uma escola que proibiu smartphones encontrou uma redução de 17% nos sintomas associados à depressão.
Fonte: Canal 4
A Austrália viu um declínio de 63% em “incidentes críticos envolvendo mídias sociais” após a proibição de telefones em escolas estaduais.
Fonte: Governo da Austrália do Sul
As crianças em escolas com uma proibição efetiva obtiveram resultados no GCSE que foram de 1 a 2 graus mais altos.
Fonte: Policy Exchange
Essas descobertas poderosas ajudaram a levar o Channel 4 a fazer um documentário sobre o uso do telefone nas escolas do Reino Unido. Se você perdeu, pode ler nossa redação sobre a escola que proibiu os smartphones.